SURGICAL EXTRACTION- PAINLESS TOOTH REMOVAL
What is Surgical Extraction?
Surgical extraction is a procedure where a tooth is removed through a surgical incision made in the gum tissue. This method is used when the tooth is not accessible through a standard extraction technique, often due to issues such as:
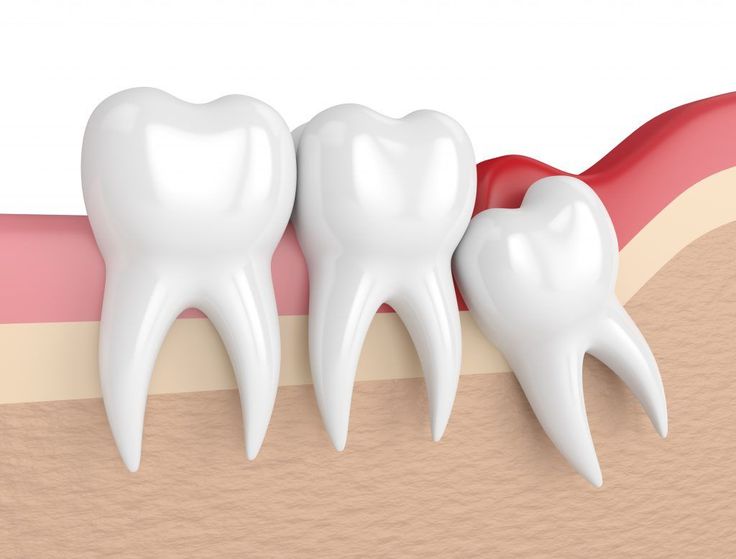
- Impacted Teeth: Teeth that are trapped beneath the gum line or bone and unable to erupt properly, such as wisdom teeth.
- Severely Broken or Decayed Teeth: Teeth that are too damaged or decayed to be removed with standard extraction tools.
- Teeth with Complex Roots: Teeth with roots that are curved or unusually shaped, making them difficult to grasp and remove.
The Procedure for Surgical Extraction
Pre-Procedure Consultation:
- Before the procedure, your dentist or oral surgeon will evaluate your dental and medical history, perform a clinical examination, and may take X-rays to assess the position and condition of the tooth and surrounding structures.
Anesthesia:
- To ensure a painless experience, local anesthesia is administered to numb the area around the tooth. In some cases, sedation or general anesthesia may be used, especially if the procedure is more complex or if the patient prefers to be less aware of the procedure.
Incision:
- The dentist or oral surgeon makes a small incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth and underlying bone. If the tooth is impacted, the incision allows the surgeon to reach and remove it more easily.
Tooth Removal:
- The tooth is carefully extracted, which may involve removing some surrounding bone or sectioning the tooth into smaller pieces for easier removal.
Closure:
- After the tooth is removed, the incision site is cleaned, and the gum tissue is stitched with dissolvable sutures if necessary. This helps to promote healing and close the wound.
Post-Procedure Care:
- Instructions for post-operative care are provided, including recommendations for pain management, oral hygiene, and dietary restrictions.
Benefits of Surgical Extraction
Effective Removal of Complex Teeth: Surgical extraction allows for the removal of teeth that are not easily accessible through standard extraction methods.
Minimized Risk of Complications: By carefully exposing the tooth and surrounding structures, surgical extraction can minimize the risk of damaging adjacent teeth, nerves, or bone.
Enhanced Healing: Proper surgical techniques and post-operative care can lead to quicker healing and reduced risk of infection.
Managing Pain and Discomfort
Anesthesia and Sedation: The use of local anesthesia and sedation ensures that you remain comfortable and pain-free during the procedure. If you experience anxiety about the procedure, discuss sedation options with your dentist.
Pain Management: Post-operative pain is typically managed with over-the-counter or prescription pain medications. Your dentist will provide guidance on how to take these medications effectively.
Swelling and Bruising: Some swelling and bruising are normal after a surgical extraction. Applying ice packs to the outside of the face and keeping your head elevated can help reduce these symptoms.
Follow-Up Care: Adhering to the post-operative care instructions provided by your dentist, including keeping the extraction site clean and avoiding certain foods and activities, is crucial for a smooth recovery.
Avoiding Complications: Following your dentist’s instructions carefully helps prevent complications such as dry socket, which occurs when the blood clot protecting the extraction site becomes dislodged.
The Team
Our Experts




