CROWN & BRIDGE
What is a Crown?
A crown is a dental prosthetic that covers or “caps” a damaged or weakened tooth. It is used to restore the tooth’s shape, size, strength, and appearance. Crowns are typically made from materials such as porcelain, ceramic, metal, or a combination of these materials.
Types of Crowns:
Porcelain Crowns: These crowns are highly aesthetic and mimic the natural appearance of teeth. They are often used for front teeth where appearance is crucial.
Ceramic Crowns: Made from durable ceramic materials, these crowns are also aesthetically pleasing and are used in visible areas of the mouth.
Metal Crowns: These crowns, made from metals like gold or alloy, are extremely durable and wear-resistant. They are often used for molars where strength is more important than appearance.
Porcelain-Fused-to-Metal (PFM) Crowns: These crowns combine the strength of metal with the aesthetic appeal of porcelain. They are suitable for both front and back teeth.
Zirconia Crowns: Made from zirconium oxide, these crowns are known for their strength, durability, and natural appearance. They are a popular choice for many patients.

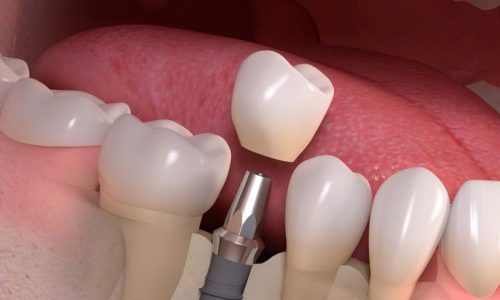
Benefits of Crowns:
- Restores Function: Crowns restore the ability to chew and bite properly, improving oral function.
- Protects Weakened Teeth: They protect teeth that are weakened by decay, large fillings, or trauma.
- Enhances Appearance: Crowns improve the appearance of discolored, misshapen, or damaged teeth.
- Durability: Crowns offer a long-lasting solution for dental restoration.
What is a Bridge?
A bridge is a dental prosthetic used to replace one or more missing teeth. It consists of one or more artificial teeth (pontics) anchored to adjacent natural teeth or dental implants. The adjacent teeth, known as abutments, are crowned to support the bridge.

Types of Bridges:
Traditional Bridges: These are the most common type of bridge, consisting of a false tooth or teeth anchored by crowns on the adjacent natural teeth.
Cantilever Bridges: Used when there is only one adjacent tooth available for anchoring. The bridge is supported at one end by a single abutment.
Maryland Bridges (Resin-Bonded Bridges): These bridges use a metal or porcelain framework with wing-like extensions that are bonded to the back of the adjacent teeth, preserving more of the natural tooth structure.
Implant-Supported Bridges: These bridges are anchored by dental implants rather than natural teeth. They are used when multiple adjacent teeth are missing and provide a stable, long-term solution.
Benefits of Bridges:
- Restores Missing Teeth: Bridges replace missing teeth, restoring the ability to chew, speak, and smile confidently.
- Prevents Tooth Shifting: They prevent adjacent teeth from shifting into the gap left by missing teeth, which can cause alignment issues.
- Improves Aesthetics: Bridges enhance the appearance of the smile by filling gaps left by missing teeth.
- Maintains Jaw Alignment: Replacing missing teeth with a bridge helps maintain the proper alignment of the jaw and bite.

The Crown and Bridge Procedure
Initial Consultation: Your dentist will examine your teeth and take X-rays to determine the appropriate treatment. They will discuss the options and decide on the best material and type of crown or bridge for your needs.
Tooth Preparation: For a crown, the damaged tooth is reshaped to accommodate the crown. For a bridge, the adjacent teeth are prepared and reshaped to support the bridge.
Impressions: Impressions or digital scans of your teeth are taken to create custom crowns or bridges that fit perfectly.
Temporary Restoration: While the permanent crown or bridge is being made, your dentist may place a temporary crown or bridge to protect the prepared teeth and maintain function.
Fitting and Bonding: Once the permanent crown or bridge is ready, it is placed and adjusted for fit, comfort, and appearance. The crown or bridge is then securely bonded to the prepared teeth or implants.
Follow-Up: Regular follow-up visits are necessary to ensure that the crown or bridge is functioning correctly and to check for any adjustments needed.
Maintenance and Care
- Oral Hygiene: Maintain excellent oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly to prevent decay and gum disease around crowns and bridges.
- Regular Check-Ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to ensure the longevity of your crown or bridge.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Be cautious with hard or sticky foods that may damage the prosthetics.




The Team
Our Experts




